Unlocking the therapeutic potential of antisense oglionucleotides and other biologics.
CHALLENGE & GOAL
More than four decades have passed since scientists revealed that antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) have the potential to treat multiple, serious diseases. Despite early excitement, experimental ASOs have faced challenges, hampered by inadequate biological activity and preclinical toxicology.¹ A technology that overcomes these challenges would pave the way for an expansive list of targeted new therapies.
SOLUTION
SRI’s FOX Three Molecular Guidance System (MGS)™ platform identifies unique, engineered peptides that can deliver any cargo directly to selected cell types and then traffic the cargo to subcellular locations within the cell. ASOs loaded onto this novel platform have been successfully delivered to and internalized by targeted, diseased cells, resulting in increased intracellular potency.
By binding to RNA within diseased cells, ASOs can reduce production of over-expressed proteins that are associated with disease.² However, to be effective as medical therapies, ASOs need to very specifically target and then be able to internalize into the desired cell types. These requirements have proven challenging and, despite sound scientific rationale for their use and early promise, ASO research continues to look for the optimal intracellular delivery options.
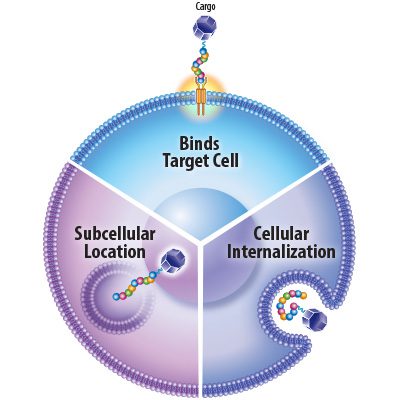
SRI’s FOX Three MGS platform has demonstrated potential to enable a new era of ASO research and therapies. In a recent study, cancer-specific MGS peptides successfully delivered anti-cancer ASOs to specific sub-cellular locations in lung cancer cells.
Researchers discovered that, upon binding to the targeted cancer cells, MGSs triggered rapid cellular uptake and trafficking of their ASO cargo. MGS delivery of ASOs increased their potency in targeted cells, while simultaneously reducing any antisense activity in non-targeted cells. These findings suggest that the FOX Three platform may uniquely address the decades-long challenge of ASO delivery.
¹ Frazier KS. “Antisense oligonucleotide therapies: the promise and the challenges from a toxicologic pathologist’s perspective.” Toxicol Pathol. 2015 Jan;43(1):78-89. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25385330
² Shen X, Corey DR. “Chemistry, mechanism and clinical status of antisense oligonucleotides and duplex RNAs.” Nucleic Acids Research. 2018 Feb; 46(4):1584–1600. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1239



