Citation
Ng, H. H., Stock, H., Rausch, L., Bunin, D., Wang, A., Brill, S., … Mirsalis, J. C. (2015). Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Toxicity, Toxicokinetics, and Toxicogenomics Analysis After 13 Weeks of Oral Administration in Mice. International Journal of Toxicology, 34(1), 4–10.
Abstract
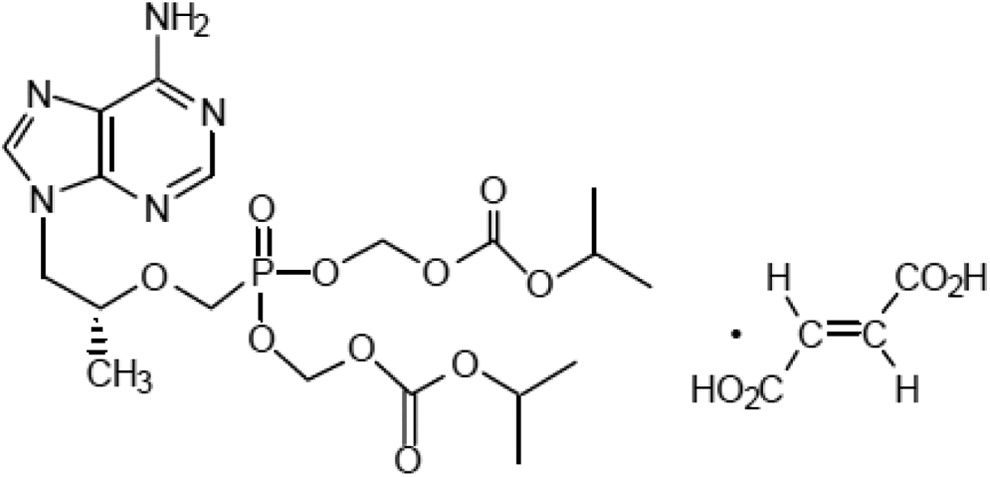
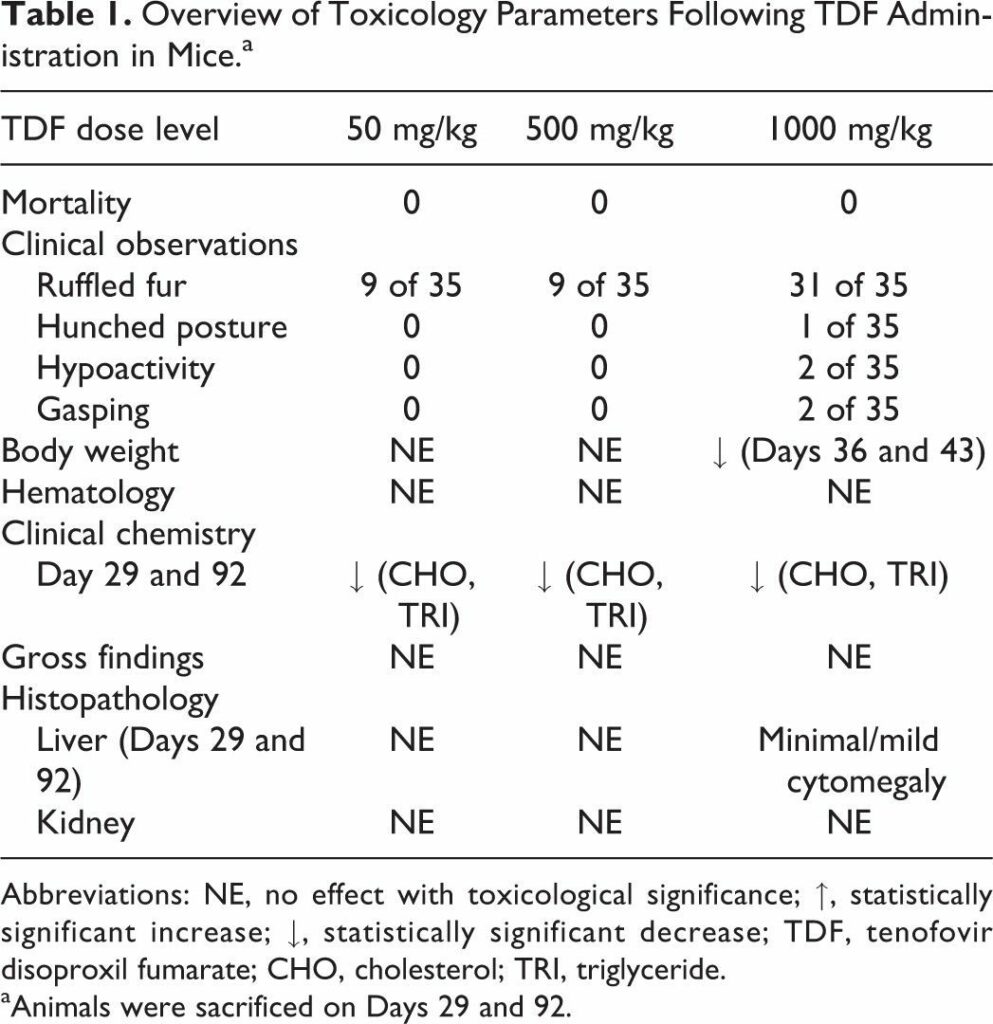
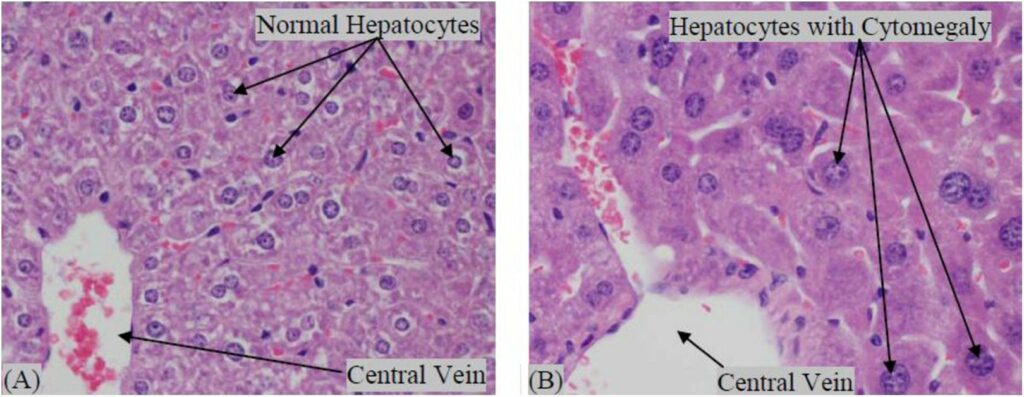
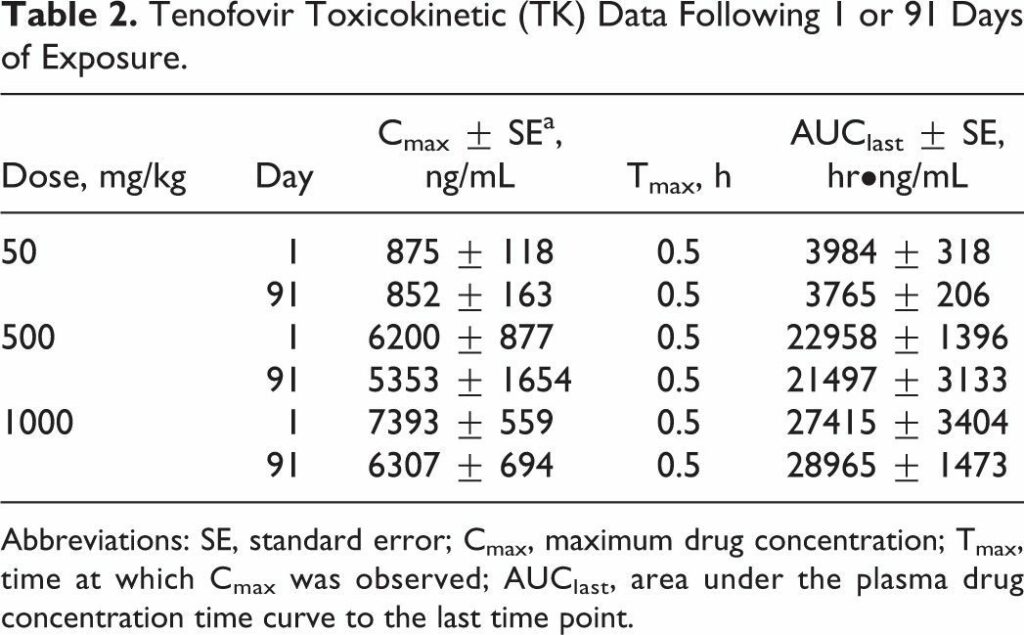
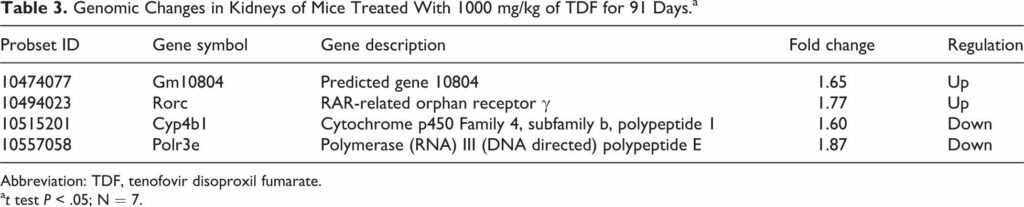
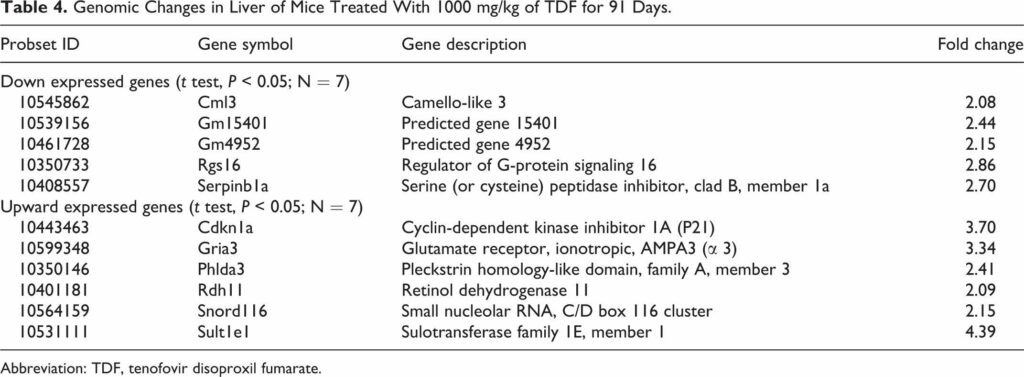
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is a prodrug of tenofovir that exhibits activity against HIV and hepatitis B. The goals of this study were to evaluate the molecular mechanism of TDF-induced toxicity in mice after 13 weeks of daily oral administration (50-1000 mg/kg) by correlating transcriptional changes with plasma drug levels and traditional toxicology end points. Plasma levels and systemic exposure of tenofovir increased less than dose proportionally and were similar on days 1 and 91. No overt toxicity was observed following the completion of TDF administration. The kidneys of TDF-treated mice were histopathologically normal. This result is consistent with the genomic microarray results, which showed no significant differences in kidney transcriptional levels between TDF-treated animals and controls. In liver, after 4 and 13 weeks, cytomegaly was observed in mice treated with 1000 mg/kg of TDF, but mice recovered from this effect following cessation of administration. Analysis of liver transcripts on day 91 reported elevated levels of Cdkn1a in TDF-treated animals compared with controls, which may have contributed to the inhibition of liver cell cycle progression.