XDR weld visualization technology gives welders full 3D view of workspace, as smart helmet collects data to help train new technicians.
CHALLENGE & GOAL
Light-blocking filters on traditional welding helmets protect welders’ eyes at the cost of visibility and productivity. As a result, welders need years to perfect their craft at a time when the Japanese construction industry already struggles with labor shortages. Kawada Technologies turned to SRI International to create a new welding helmet that would improve productivity, increase safety and help train future generations of welding technicians.
SOLUTION & OUTCOME
SRI developed a 3D welding helmet that uses image processing to give technicians an unobstructed view of the entire workspace during arc welding. The new Extreme Dynamic Range weld visualization technology (XDR) enables technicians to weld more efficiently and reliably, and it provides new technicians the equivalent of years of experience.
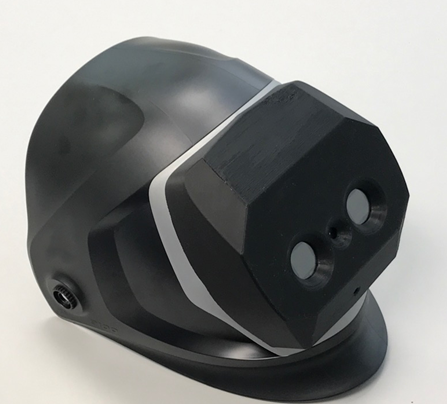

Kawada Industries, a subsidiary of Kawada, is one of the leading construction and bridge-building firms in Japan that manufactures many of the thick steel plates joined by arc welding. KTI Kawada Group partnered with SRI to develop new technology that would greatly shorten the time required to teach new technicians and pass down welding knowledge gained on the job.
SRI applied advanced vision technologies to invent XDR weld visualization technology, which uses small camera modules and image fusion techniques to display an XDR composite image in stereo vision, or 3D. The new 3D welding helmet provides a much larger field of view than conventional welding helmets, enabling inexperienced welders to easily collect and check useful information to ensure a high-quality weld. XDR also can capture images of the welder’s line of sight as data for future analysis, accelerating the learning curve for the individual welder and future technicians.
XDR controls the shutter speed and the time at which images are captured at 1/1000 seconds, and it acquires images at the same angle of view with different exposure conditions to avoid both under — and overexposure of the images. A GPU processes the captured frames to synthesize the frames in real time into one frame.
The image below shows the XDR view on the left, as opposed to the view from a traditional welding helmet, as shown on the right.
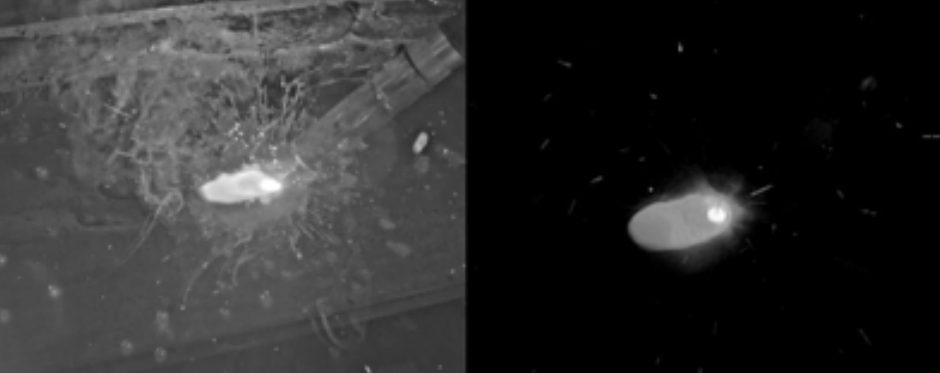
The 3D welding helmet greatly improves both the scope and detail of the welder’s view, enabling technicians to weld more reliably. The helmet also includes display and save functions for various parameters related to welding — particularly helpful for inexperienced welders who now can easily collect and check useful information.
Kawada continues to refine the 3D welding helmet and will use it to teach technical welding skills. The company also is working on analyzing data obtained by the helmets to support new technological and product developments and improve the overall quality and reliability of welding.



