Human behavior modeling
CVT’s human behavior modeling centers around three aims: 1) human behavior monitoring, 2) human interaction/communication and 3) facilitation. CVT has developed a layered approach to human behavior analytics that enabled development of the core technologies that address all three aims.
Human state assessment
CVT has developed real-time behavior detection, including gaze estimation, facial expression recognition, gesture recognition and posture recognition as part of SRI’s Multimodal Integrated Behavior Analytics (MIBA) software system. MIBA has been used with two different social interaction systems in which the user has fluid human-like multimodal interaction with virtual characters and learns social interaction skills.
CVT under Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) funding has developed driver behavior analytics (DCODE) such as gaze, facial expressions, etc., as well as analytics for situational awareness outside the vehicle, such as monitoring of signaling by other vehicles, traffic lights, warning signs, etc. CVT also developed masking technology (DMASK) to anonymize video content with drivers that preserves the facial expressions and other behaviors in a virtual mask that covers the face to prevent face recognition.
CVT has expanded the driver behavior analytics under a project with Toyota Motor Corporation in which we developed techniques for assessing driver emotional states as well as drowsiness. These were enabled by gaze tracking, facial expression extraction, and blink rate extraction. Note that the automotive environments possess formidable lighting and pose variation challenges.

Assessment of collaboration
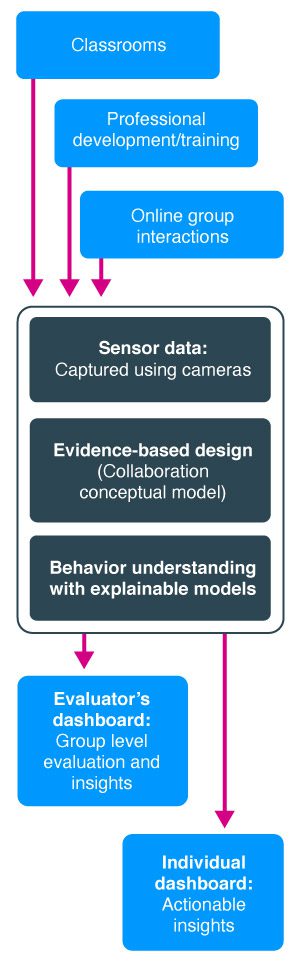
CVT has been working towards a solution to monitor collaboration in classrooms by further developing our layered behavior analytics. CVT has built on the low-level behaviors captured by MIBA to build more levels starting from individual behaviors such as problem solving, group dynamics as well as role-playing, to arrive at the level of overall assessment of the group’s collaborative state. Such a layered architecture enables fine-grained feedback to the teacher and their students to improve collaboration. This work has been featured in the National Science Foundation (NSF) showcase.
Communicating with computers
Under the DARPA Communicating with Computers (CwC) program, CVT has developed an interactive blocks world environment, called SMILEE, in which the user collaborates with the computer on building real-world block patterns. Here we both model the task as well as the verbal and non-verbal behavior of the user.
Intelligent AR based interactive systems
SRI has developed an AR-Mentor systems for providing guidance to users doing complex tasks.
AR-Mentor is a wearable real time Augmented Reality (AR) mentoring system that is configured to assist in performing complex tasks including maintenance and repair tasks of complex machinery, such as vehicles, appliances, and industrial machinery. The system combines a wearable Optical-See-Through (OST) or Video-See-Through (VST) display device with high precision 6-Degree-Of-Freedom (DOF) pose tracking and a virtual personal assistant (VPA) with natural language, verbal conversational interaction, providing guidance to the user in the form of visual, audio and locational cues. The system is designed to be heads-up and hands-free allowing the user to freely move about the maintenance or training environment and receive globally aligned and context aware visual and audio instructions (animations, symbolic icons, text, multimedia content, speech). The user can interact with the system, ask questions and get clarifications and specific guidance for the task at hand.
SRI has developed AR-Mentor systems for multiple applications including repair and maintenance, training systems for students with dyslexia, and guiding farmers monitor crop growth for agriculture.
Recent work
-

SRI’s classroom collaboration NSF Project on Understanding STEM Collaboration
The Automated Collaboration Assessment Using Behavioral Analytics project will measure and support collaboration as students engage in STEM learning activities.
-

SRI’s MIBA real-time behavior analytics system
The system is applicable to a wide variety off Human Computer Interaction applications including most recently, social interaction training through fluid life like interaction with Non-Player Characters in a virtual…
-

Award-winning Driver Monitoring System helps improve safety
SRI researchers teach AI system to recognize human emotional states and react accordingly
Recent publications
-
Towards Understanding Confusion and Affective States Under Communication Failures in Voice-Based Human-Machine Interaction
We present a series of two studies conducted to understand user’s affective states during voice-based human-machine interactions.
-
Towards Explainable Student Group Collaboration Assessment Models Using Temporal Representations of Individual Student Role and Behavioral Cues
In this paper we propose using simple temporal-CNN deep-learning models to assess student group collaboration that take in temporal representations of individual student roles as input.
-
Human Motion Modeling using DVGANs
We present a novel generative model for human motion modeling using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
